Factoring Business in India is regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). All factoring companies and non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) engaged in factoring business are required to obtain a registration certificate from the RBI to operate within the regulations set by the authority.
Factoring is considered an important source of short-term and working capital financing for micro, small, and medium enterprises in India, and the RBI oversees and governs the industry to ensure fair practices and protection for all parties involved. This regulatory framework provides guidelines and standards to maintain the integrity and efficiency of the factoring business in India.
Credit: vinodkothari.com
Introduction To Factoring Business
Factoring business in India is regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). Companies engaged in factoring must obtain a registration certificate from the RBI and adhere to the regulations set by the authority. Factoring is an important source of short-term financing for micro, small, and medium enterprises in India.
Definition Of Factoring
Factoring refers to a financial arrangement where businesses sell their accounts receivable to a third-party financial institution known as a factor. In return, the factor provides immediate cash to the business, allowing them to meet their short-term working capital needs. It is essentially a form of receivables financing where businesses can turn their invoices into cash without waiting for their customers to make the payment. Factoring is a widely used financing option in India, particularly by micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs), as it helps improve cash flow and provides them with the necessary funds to run their operations smoothly.Importance Of Factoring In India
Factoring plays a crucial role in the Indian business landscape, especially for MSMEs. Here is why factoring holds enormous importance in India: 1. Improved Cash Flow: Factoring allows businesses to convert their outstanding invoices into immediate cash, providing them with a regular and predictable cash flow. This improved liquidity helps businesses meet their daily expenses, pay their suppliers on time, and invest in growth opportunities. 2. Working Capital Management: Lack of working capital is a major challenge faced by many businesses in India. Factoring helps businesses address this issue by providing them with access to immediate funds. With a stable source of working capital, businesses can efficiently manage their operations, meet payroll, and invest in inventory without relying heavily on traditional loans or overdraft facilities. 3. Reduced Credit Risk: Through factoring, businesses transfer the credit risk associated with their accounts receivable to the factor. This means that if a customer fails to make payment on an invoice, the business is not responsible for the loss. This protection against bad debt helps businesses mitigate credit risk and focus on their core operations instead of chasing payments. 4. Growth Opportunities: Factoring provides businesses with the necessary liquidity to seize growth opportunities such as expanding operations, launching new products, or entering new markets. By unlocking the cash tied up in their invoices, businesses can invest in their growth strategies and stay competitive in the market. In conclusion, factoring is a regulated financial practice in India that offers numerous benefits to businesses, especially MSMEs. By converting their accounts receivable into immediate cash, businesses can improve their cash flow, efficiently manage working capital, reduce credit risk, and seize growth opportunities.
Credit: m.facebook.com
Regulation Of Factoring Business In India
The factoring business in India is regulated by various authorities to ensure transparency, fair practices, and the protection of stakeholders’ interests. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) plays a crucial role in setting guidelines and regulations for the factoring industry. Additionally, the registration of Factor NBFCs and companies is mandatory to operate in this sector. The government also enforces regulations to maintain a conducive environment for factoring operations. Let’s delve into each aspect of the regulation of factoring business in India.
Rbi Guidelines For Factoring
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has laid down comprehensive guidelines for the functioning of the factoring industry. These guidelines cover various aspects, including eligibility criteria, prudential norms, risk management, operational standards, and reporting requirements. By mandating compliance with these guidelines, the RBI ensures that all participants in the factoring business adhere to industry best practices and maintain transparency in their operations.
The RBI guidelines also address the financing needs of micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs), recognizing factoring as an important source of short-term and working capital financing for these entities. By providing a regulatory framework, the RBI fosters a favorable environment for factoring activities, thus facilitating the growth of the sector and supporting the financial needs of MSMEs.
Registration Of Factor Nbfcs And Companies
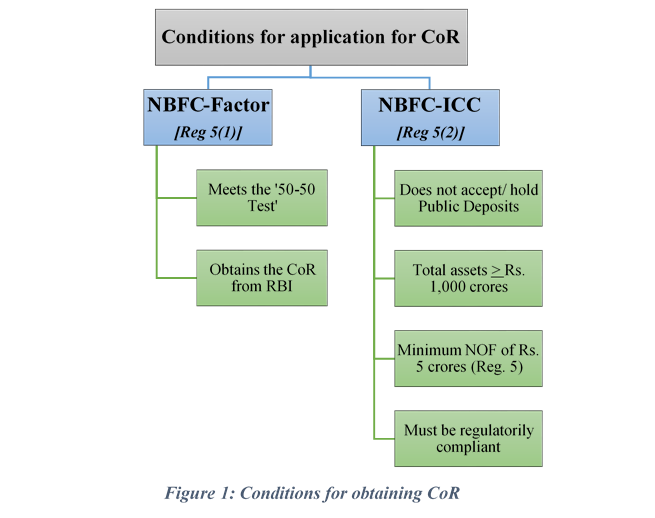
According to the regulations issued by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), Factor Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) and companies engaged in factoring business must obtain a registration certificate. This registration is a mandatory requirement to operate in the factoring industry. The RBI’s registration process ensures that only credible and compliant entities are permitted to engage in factoring activities.
| Registration Process Highlights: |
|---|
| 1. Submitting application and necessary documentation to the RBI |
| 2. Meeting the eligibility criteria specified by the RBI |
| 3. Complying with the prudential norms and operational standards set by the RBI |
| 4. Obtaining a registration certificate from the RBI upon successful evaluation |
Government Regulations For Factoring
In addition to the RBI guidelines, the government of India enforces regulations to ensure the smooth and transparent functioning of the factoring industry. These regulations aim to create a conducive environment for factoring operations, promote fair competition, and safeguard the interests of all stakeholders involved.
The government’s regulations cover various aspects, including licensing requirements, compliance with anti-money laundering measures, dispute resolution mechanisms, and the prevention of fraudulent practices. By enacting and enforcing these regulations, the government safeguards the integrity and stability of the factoring business in India, while also instilling trust among market participants.
Role Of Rbi In Factoring Regulation
Factoring business in India is regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). Companies engaged in factoring must obtain a registration certificate from the RBI to operate in accordance with the regulations set by the authority. The RBI plays a crucial role in overseeing and governing the factoring industry in India.
Factoring is a popular financing option for businesses in India, especially small and medium enterprises (SMEs). It provides them with immediate access to funds by selling their invoices to a third party known as a factor. To ensure smooth and regulated operations of the factoring business in India, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) plays a crucial role. The RBI has implemented guidelines and regulations that govern the operations of factoring companies in the country. Let’s explore the responsibilities of the RBI in factoring regulation and its role in monitoring factoring companies.Responsibilities Of Rbi
The RBI is responsible for overseeing and regulating the financial sector in India, and factoring is no exception. When it comes to factoring regulation, the RBI has a set of responsibilities to ensure the smooth functioning of the industry. These responsibilities include:- Issuing guidelines and regulations: The RBI issues guidelines and regulations that govern the operations of factoring companies in India. These guidelines outline the eligibility criteria, registration requirements, prudential norms, and other operational aspects for factoring companies.
- Registration of factor NBFCs and companies: Under these regulations, the RBI has made it mandatory for factor non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) and companies to obtain a registration certificate. This registration ensures that only authorized and compliant entities can carry out factoring business in India.
- Monitoring compliance: The RBI monitors the compliance of factoring companies with the issued guidelines and regulations. It conducts regular inspections, audits, and assessments to ensure that the companies adhere to the set norms and maintain financial stability.
- Addressing grievances: The RBI also plays a crucial role in addressing grievances related to factoring services. It sets up mechanisms and guidelines for customers and stakeholders to file complaints against factoring companies and ensures their timely resolution.
Rbi’s Role In Monitoring Factoring Companies
Apart from its responsibilities, the RBI plays a vital role in monitoring the operations of factoring companies in India. Its role in monitoring includes:- Inspections and audits: The RBI conducts regular inspections and audits of factoring companies to assess their financial health, risk management practices, and compliance with regulatory requirements. These inspections help in identifying any potential risks and taking corrective measures to protect the interests of factoring clients.
- Enforcement actions: In case of any non-compliance or violations of the regulations, the RBI has the authority to take enforcement actions against factoring companies. These actions may include fines, penalties, suspension, or cancellation of registration, depending on the severity of the non-compliance.
- Guidance and supervision: The RBI provides guidance and supervision to the factoring companies to ensure their smooth operations and adherence to regulations. It conducts regular meetings, workshops, and seminars to update them on any changes in the guidelines and address their queries and concerns.

Credit: www.yumpu.com
Benefits And Challenges Of Factoring Regulation
The regulation of factoring business in India is crucial for maintaining transparency and protecting the rights of all parties involved. It brings about several benefits while also presenting certain challenges. Understanding the advantages and obstacles of factoring regulation is essential for businesses operating in India.
Advantages Of Regulation
Regulating the factoring business in India offers numerous advantages, contributing to a more stable and secure environment. Some key benefits include:
- Enhanced trust and confidence among businesses and financial institutions
- Protection of the rights of all parties involved, including the sellers, buyers, and financiers
- Establishment of standard practices and procedures, ensuring consistency and reliability
- Reduction in the risk of fraudulent activities and disputes
Challenges In Implementing Factoring Regulation
While factoring regulation brings about several benefits, its implementation also poses certain challenges. These challenges may include:
- Ensuring compliance across diverse regions and sectors within the country
- Addressing the complexities associated with varying business practices and legal frameworks
- Overcoming resistance or reluctance from some industry participants towards regulatory changes
- Enforcement and monitoring of compliance to mitigate potential violations and non-compliance
Future Outlook For Factoring Business In India
Factoring business in India is regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), which plays a crucial role in overseeing and maintaining the stability of the financial sector. The regulation provided by the RBI ensures that factoring companies operate within a framework that promotes transparency, efficiency, and fair practices. This regulatory oversight is essential for the healthy growth of the factoring industry in India.
Growth Potential Of Factoring In India
The factoring industry in India holds significant potential for growth, especially in catering to the financing needs of micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs). The growth potential is driven by the increasing demand for working capital financing and the need for efficient cash flow management among businesses. As the economy continues to expand, factoring services are expected to play a crucial role in supporting the growth of businesses, thereby contributing to the overall development of the Indian economy.
Measures To Further Strengthen Factoring Regulation
To further strengthen the regulation of factoring business in India, it is imperative to enhance collaboration between regulatory authorities and industry stakeholders. This can be achieved through the implementation of robust reporting mechanisms, regular audits, and the promotion of best practices. Additionally, continuous efforts in educating and creating awareness among market participants about the regulatory framework will help in fostering a more compliant and ethical factoring ecosystem.
Frequently Asked Questions For Factoring Business In India Is Regulated By
What Is The Factoring Regulation In India?
Factoring regulation in India is governed by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). Companies engaged in factoring business are required to obtain a registration certificate from the RBI. The RBI provides guidelines and regulations for the operation of factoring services in India.
Factoring companies also rely on self-regulation and best practices encouraged by associations such as the International Factoring Association and the Commercial Finance Association.
Which Agency Governs Factoring Services In India?
Factoring services in India are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). Factors must obtain a registration certificate from the RBI to engage in factoring business. This ensures compliance with regulations issued by the RBI.
Who Governs Factoring Companies?
Factoring companies in India are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India. Companies must obtain a registration certificate from the RBI to engage in factoring business. The International Factoring Association and Commercial Finance Association also provide guidance and tools for their members.
What Are The Rbi Guidelines On Factoring?
Factoring companies in India are required to obtain a registration certificate from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to carry out factoring business, as per the regulations issued by the authority. This ensures compliance with the RBI guidelines on factoring.
Conclusion
Factoring business in India is regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). To engage in factoring business, companies are mandatorily required to obtain a registration certificate from the RBI. The RBI guidelines on factoring ensure that the industry operates in a regulated and transparent manner.
This regulatory framework provides confidence and protection to both factoring companies and their clients. By adhering to these guidelines, the factoring industry in India can continue to serve as an important source of short-term financing for micro, small, and medium enterprises.