Factoring in business studies involves a company selling its accounts receivables at a discounted price to a third party, allowing the company to access immediate cash from unpaid invoices. Also known as invoice factoring, this practice helps businesses free up capital without having to wait for payment terms.
It is a form of financing agreement in which a creditor purchases the credit risk or rights to a company’s accounts receivable instead of the company seeking a traditional bank loan. Factoring plays a vital role in trade finance, where sellers sell their outstanding invoices at a discount to a finance provider, known as the ‘factor’.
This type of finance assists businesses in meeting their short-term liquidity needs by selling their accounts receivable to a third party. Factors pay the amount due on the invoices, minus their commission or fees.
Introduction To Factoring Business Studies
Factoring is a financial technique commonly used by businesses to improve their cash flow and manage their accounts receivable. It involves selling accounts receivable to a third party, known as a factor, at a discounted rate in exchange for immediate cash. This allows businesses to access the funds tied up in unpaid invoices without having to wait for the usual payment terms.
Definition Of Factoring
Factoring, also known as invoice factoring or accounts receivable financing, is a financing method that enables businesses to convert their accounts receivable into immediate cash. It involves selling the rights to collect payments on outstanding invoices to a third party, the factor, at a discount. The factor then assumes the responsibility of collecting the payments from the customers.
Benefits Of Factoring
- Improved Cash Flow: Factoring provides businesses with immediate cash, allowing them to cover expenses and invest in growth opportunities.
- Reduced Credit Risk: By selling their receivables, businesses transfer the credit risk to the factor, protecting themselves from non-payment or delayed payment by customers.
- Focus on Core Operations: Factoring eliminates the need for businesses to spend time and resources on accounts receivable management, allowing them to focus on their core operations.
Examples Of Factoring In Business Studies
| Industry | Factoring Example |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing | A manufacturing company sells its outstanding invoices to a factor, which provides immediate cash to cover production costs and invest in new equipment. |
| Construction | A construction firm factors its receivables to maintain a steady cash flow and meet payroll obligations while waiting for payment from clients. |
| Wholesale Distribution | A wholesale distributor uses factoring to finance its inventory purchases and fulfill large orders from retailers. |
Understanding Debt Factoring
Debt factoring is a vital concept in business studies, especially when it comes to managing cash flow and maximizing liquidity. In this section, we will delve into the definition of debt factoring, how it works, as well as the advantages and disadvantages it offers to businesses.
Definition Of Debt Factoring
Debt factoring, also known as invoice factoring, is a financial arrangement where a business sells its accounts receivable to a third-party company, known as a factor, at a discounted rate. It allows businesses to gain immediate access to the funds tied up in unpaid invoices, without having to wait for the usual payment terms.
How Debt Factoring Works
Debt factoring works in a straightforward manner. When a business decides to utilize debt factoring, it starts by selecting a reputable factor. Once the factor is chosen, the business sells its outstanding invoices to the factor at a discount. The factor then takes over the responsibility of collecting the payment from the customers on behalf of the business.
The factor typically provides an advance payment to the business, which is usually a percentage of the total value of the invoices. The remaining amount, minus the factor’s fees, is paid to the business once the customers settle their invoices. This process helps businesses overcome cash flow issues and ensures a steady inflow of funds.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Debt Factoring
Debt factoring offers several advantages and disadvantages that businesses should consider before opting for this financing arrangement.
Advantages:
- Improved Cash Flow: Debt factoring provides immediate access to cash, allowing businesses to cover operational expenses, invest in growth opportunities, and reduce reliance on credit.
- Reduced Bad Debt Risk: By transferring the responsibility of collecting payments to the factor, businesses mitigate the risk of bad debts and non-payment from customers.
- Efficient Receivables Management: Factors are experts in managing accounts receivable. They have robust systems in place to track and collect payments, which saves businesses time and effort.
- Flexible Financing: Debt factoring does not create additional debt on the balance sheet of the business since it involves selling the invoices rather than obtaining a loan.
Disadvantages:
- Decreased Profitability: The discount offered by the factor reduces the total amount received by the business, which can impact profitability.
- Loss of Control over Customer Relationships: When the factor takes over the collection process, the business may lose direct contact with its customers, potentially affecting customer relationships.
- Confidentiality Concerns: Some businesses may have concerns about disclosing their financial information to the factor, which is a necessary part of the debt factoring process.
- Cost: Factors charge fees for their services, which can be higher than the interest rate on traditional loans.
Despite the disadvantages, debt factoring can be a valuable tool for businesses in managing their cash flow and ensuring smooth operations. By carefully evaluating the pros and cons, businesses can make an informed decision on whether debt factoring is the right finance option for them.
Factoring In Business Law
Factoring in business law is a type of financing arrangement where a creditor purchases the rights to a company’s accounts receivable or the credit risk associated with them. Instead of obtaining a loan from a bank, businesses have the option to sell their accounts receivable to a creditor in exchange for immediate cash or to improve their balance sheets.
Definition Of Factoring In Business Law
Factoring in business law is a financing agreement where a creditor buys the rights to a company’s accounts receivable or the credit risk associated with them. This allows businesses to access immediate cash or improve their balance sheets without taking on additional debt.
Credit Risk And Balance Sheets
When a company engages in factoring, they transfer the credit risk of their accounts receivable to a creditor. This means that the creditor assumes the responsibility for collecting payment from the customers who owe the company money. By doing so, the company can remove the credit risk from their balance sheets, which can improve their financial standing and provide a more accurate representation of their assets and liabilities.
Benefits Of Factoring In Business Law
- Immediate Access to Cash: Factoring allows businesses to unlock the cash tied up in their unpaid invoices without having to wait for the usual payment terms.
- Improved Cash Flow: By receiving immediate cash for their accounts receivable, businesses can improve their cash flow and fund their operations more effectively.
- Limited Credit Risk: When a company factors their accounts receivable, they transfer the credit risk to the creditor. This can protect the company from potential losses if their customers fail to pay.
- Focus on Core Operations: By outsourcing the collection of payments to a creditor, businesses can focus on their core operations, such as producing goods or providing services, instead of spending time and resources on credit control.
- Flexible Financing: Factoring provides businesses with a flexible financing option, as the amount of funding available depends on the value of their accounts receivable.
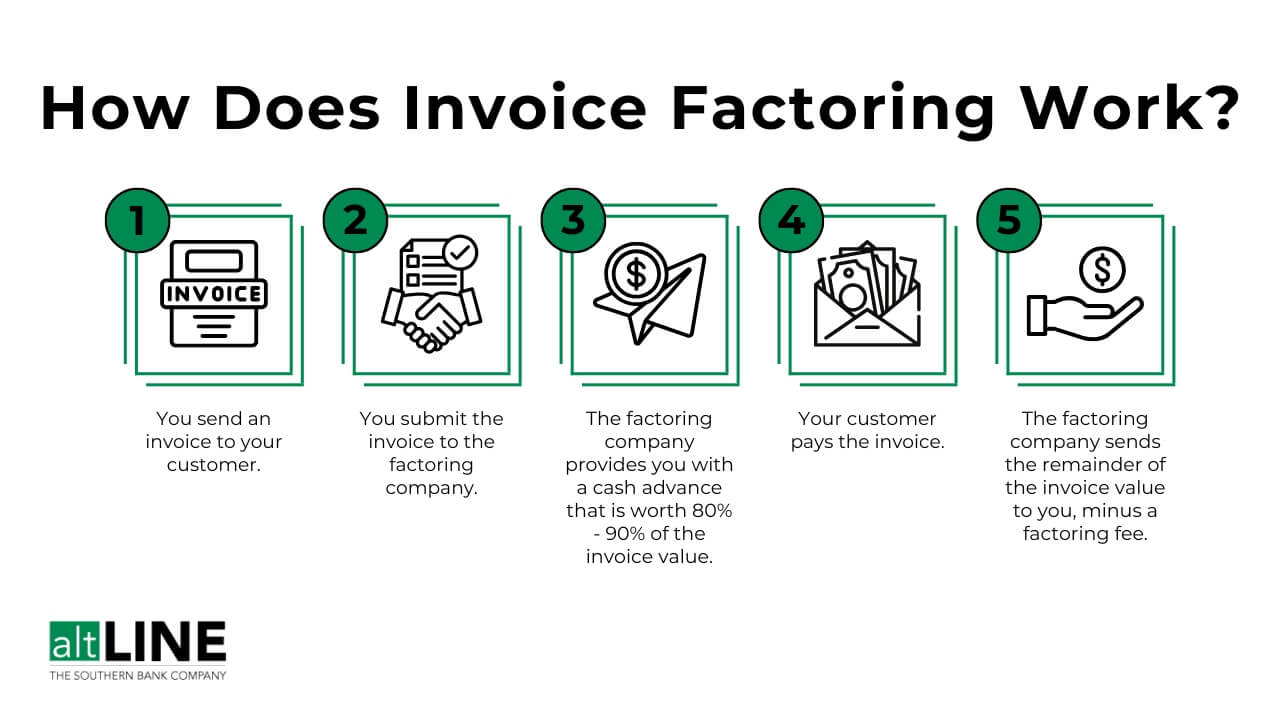
Credit: altline.sobanco.com
Factoring In Trade Finance
Factoring in trade finance plays a crucial role in facilitating international commerce and mitigating financial risks for businesses engaged in global trade transactions. Factoring in trade finance, often referred to simply as trade factoring, involves the purchase of receivables (invoices) from exporters by a specialized financial institution known as a factor, providing working capital to the exporter before the actual payment from the importer. This arrangement allows businesses to optimize their cash flow and minimize credit risk associated with cross-border transactions.
Definition Of Factoring In Trade Finance
Factoring in trade finance, also known as trade factoring, refers to the financial arrangement where a specialized financial institution, known as a factor, purchases accounts receivables or invoices from exporters at a discount, providing immediate working capital to the exporter and assuming the credit risk associated with the transaction.
Role Of Factoring In Trade Finance
Factoring plays a pivotal role in trade finance by providing exporters with immediate liquidity, enabling them to bridge the gap between the delivery of goods or services and the receipt of payment from importers. Additionally, it reduces credit risk, enhances cash flow, and allows businesses to expand their international trade operations by offering competitive terms to buyers.
Benefits Of Factoring In Trade Finance
- Enhanced Cash Flow: Factoring in trade finance provides immediate access to working capital, improving liquidity for businesses.
- Credit Risk Mitigation: Factors assume the credit risk associated with the receivables, reducing the exporter’s exposure to non-payment or insolvency of buyers.
- Facilitates International Trade: By providing upfront financing, trade factoring enables businesses to engage in cross-border trade with confidence.
- Working Capital Optimization: Factoring allows businesses to unlock the value of their accounts receivables, optimizing their working capital and operational efficiency.
Requirements And Benefits Of Factoring
Factoring is a financing arrangement where a business sells its accounts receivables to a third party at a discount, allowing them to access immediate cash from unpaid invoices. This helps companies improve cash flow without waiting for payment terms. Factoring is beneficial for businesses looking to manage working capital and maintain a steady cash flow.
Factoring is a financial transaction where a company sells its accounts receivable to a third party at a discount. This practice allows businesses to unlock cash quickly from unpaid invoices without waiting for the usual payment terms. Before choosing a factor, a business must have accounts receivable as the assets they intend to use. The business should also have customers with creditworthy reputations to ensure efficient factoring. Factoring provides numerous benefits such as immediate access to cash flow, reduction in administrative burden, and enhanced financial stability. Additionally, factoring allows businesses to quickly obtain working capital without increasing debt or diluting ownership.
Credit: www.getbraavo.com

Credit: www.invensis.net
Frequently Asked Questions On Factoring Business Studies
What Is An Example Of Factoring?
Factoring is when a business sells its unpaid invoices to a third party at a discount, allowing them to immediately access cash. It helps companies improve their cash flow by unlocking funds that would otherwise be tied up in unpaid invoices.
What Is Debt Factoring In Business Studies?
Debt factoring in business studies refers to the process of a business selling its accounts receivables to a third party at a discount. This allows the business to immediately access cash from unpaid invoices instead of waiting for payment. Debt factoring is also known as invoice factoring.
What Is Factoring In Business Law?
Factoring in business law is a financing agreement where a creditor buys a company’s accounts receivable to obtain immediate cash. Instead of getting a bank loan, a company sells its unpaid invoices to a creditor at a discount to improve their cash flow or balance sheet.
Is Factoring A Trade Finance?
Factoring is a form of trade finance where businesses sell their accounts receivable at a discount to a finance provider. It helps to immediately unlock cash tied up in unpaid invoices.
Conclusion
Factoring business studies is an essential topic for any business owner or entrepreneur. By understanding the concept of factoring and how it works, companies can unlock cash tied up in unpaid invoices and improve their liquidity. Whether it’s debt factoring or invoice factoring, the benefits of factoring are clear.
It provides immediate access to funds, improves cash flow, and allows companies to focus on their core operations. Factoring is a valuable financial tool that can help businesses thrive in today’s competitive market. Embracing factoring can lead to increased stability and growth for businesses of all sizes.