The difference between factoring and financing is that factoring involves a relationship between the lender and the client, while financing creates a relationship between the lender and the business. Both options allow business owners to collect invoice payments upfront without waiting for payment from clients.
Invoice factoring requires the business’ customer to redirect payment, while financing does not involve the customer. Invoice financing allows businesses to borrow against their outstanding invoices, while factoring involves selling the invoices to a factoring company. It’s important for business owners to consider the advantages and disadvantages of each option before making a decision.
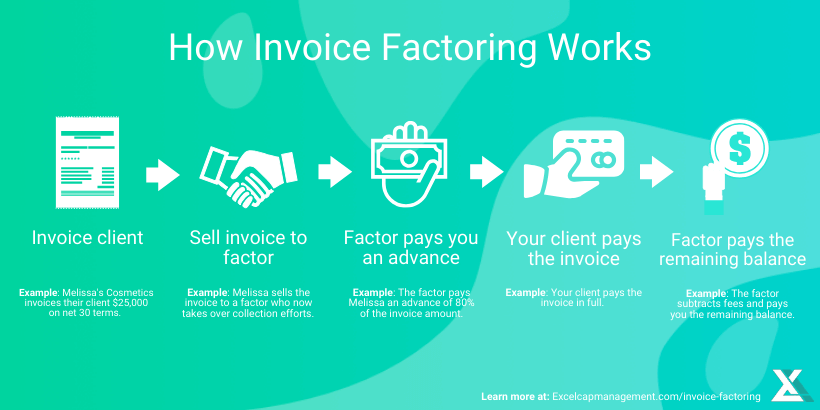
Credit: www.excelcapmanagement.com
1. Understanding Factoring And Financing
Factoring and financing are two common methods used by businesses to improve their cash flow. Both factoring and financing allow businesses to receive payment for their invoices upfront, rather than waiting for their clients to pay. However, there are key differences between these two methods that businesses need to understand.
1.1 Factoring Vs. Financing: Key Differences
One of the key differences between factoring and financing is the relationship that is created between the business and the lender. In factoring, the relationship is between the lender and the client’s customers. The lender takes temporary ownership of the receivables and is responsible for their collection. They may also provide additional services, such as invoice processing and credit checks, to save businesses time and money. On the other hand, in financing, the relationship is between the business and the lender. The lender provides funds based on the value of the invoices, but the business retains control of the receivables and is responsible for their collection.
1.2 Supplier Financing Vs. Factoring
Another important distinction to make is between supplier financing and factoring. While both methods involve receiving payment for invoices upfront, the control and initiation of the funding process differ. In supplier financing, the buyer controls the process and is responsible for initiating the funding. On the other hand, in factoring, the supplier is in charge of control and initiates the funding process. Additionally, supplier financing is not asset-based, while factoring is.
1.3 Lending Vs. Factoring
The difference between lending and factoring lies in the level of ownership the lender takes over the receivables. Lenders typically only provide funds based on the value of the invoices but do not take ownership or responsibility for their collection. In contrast, factors can take temporary or permanent ownership of the receivables and are responsible for collecting payments. Furthermore, factors may offer additional services such as invoice processing and credit checks on the client’s customers, providing added convenience and cost-saving benefits to businesses.
Overall, understanding the differences between factoring and financing, as well as the variations within each method, is crucial for businesses looking to enhance their cash flow. Whether choosing between factoring and financing or deciding between supplier financing and factoring, businesses must carefully consider their specific needs and priorities to select the best solution.

Credit: quickbooks.intuit.com
2. Pros And Cons Of Factoring
Factoring is a popular financing option for businesses looking to improve their cash flow. Like any financial strategy, factoring comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages that business owners need to consider. In this section, we will explore the pros and cons of factoring to help you make an informed decision for your business.
2.1 Advantages Of Factoring
- Improved Cash Flow: Factoring allows businesses to receive immediate cash for their outstanding invoices, providing a much-needed boost to cash flow.
- Quick Access to Funds: Unlike traditional financing options, factoring offers a quick and hassle-free process, enabling businesses to access funds within a short period.
- No Debt Accumulation: Factoring is not a loan, so businesses do not accumulate debt. Instead, they receive funds based on the value of their invoices.
- Outsourced Collections: With factoring, the responsibility of invoice collection is transferred to the factoring company, saving businesses time and resources.
- Potential for Growth: The immediate cash flow provided by factoring enables businesses to invest in new opportunities and expand their operations.
2.2 Disadvantages Of Factoring
- Higher Costs: Factoring fees can be higher compared to traditional financing options, cutting into a business’s profit margin.
- Limited Control: When factoring invoices, businesses relinquish control over the collection process to the factoring company, which may affect customer relationships.
- Dependence on Customer Creditworthiness: Factoring companies evaluate the creditworthiness of a business’s customers before approving funds, which can limit the availability of financing.
- Requirement for Continuous Factoring: Factoring is an ongoing financing arrangement that may require businesses to factor all their invoices, regardless of whether they need immediate cash for them or not.
- Potential Impact on Image: Some businesses may perceive factoring as a sign of financial instability, which could affect their reputation with customers and suppliers.
In conclusion, factoring can be a valuable financial tool for businesses with cash flow challenges, offering immediate funds without accumulating debt. However, it’s essential to consider the higher costs, limited control, and potential impact on image associated with factoring. By weighing the pros and cons, businesses can make an informed decision on whether factoring is the right financing option for their needs.
3. Pros And Cons Of Financing
In comparing factoring vs. financing, the advantage of factoring is its quick cash flow from invoices, but financing offers more control over the customer relationship and collection. However, factoring may involve redirecting payments and impacting customer involvement, while financing places the burden on the business owner to ensure cash availability.
3. Pros and Cons of Financing Financing can be a viable option for businesses in need of capital to fuel growth or manage cash flow. However, like any financial solution, it comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. In this section, we will explore the pros and cons of financing to help you make an informed decision. 3.1 Advantages of Financing Financing offers several advantages that can benefit businesses in various ways: 1. Quick access to funds: When you opt for financing, you can receive the funds you need in a relatively short period of time. This can be particularly beneficial when you have urgent financial needs, such as paying suppliers or seizing a growth opportunity. 2. Flexibility: Financing options come in various forms, including loans, lines of credit, or equipment financing. This allows you to choose the option that best suits your business needs. With this flexibility, you can obtain the capital required for specific purposes and repay it in a manner that aligns with your cash flow. 3. Retain ownership and control: Unlike some alternatives like equity financing, financing enables you to retain ownership and control of your business. You don’t need to give up shares or decision-making power to access the funds you need. 4. Build creditworthiness: By borrowing and repaying financing, you have the opportunity to build a positive credit history for your business. This can be valuable in the future when seeking additional financing or negotiating favorable terms with lenders. 3.2 Disadvantages of Financing While financing offers advantages, it also comes with certain drawbacks that you need to consider before making a decision: 1. Interest costs: Borrowing funds typically involves paying interest, which increases the overall cost of financing. It’s essential to carefully evaluate the interest rates and terms offered by lenders to ensure that the financial benefits outweigh the interest expenses. 2. Debt obligations: By opting for financing, you take on a debt obligation that needs to be repaid according to the agreed-upon terms. This means you have regular payments to make, which can put additional strain on your cash flow, especially during challenging times. 3. Qualification criteria: Lenders have specific criteria that businesses need to meet to qualify for financing. This can include factors like credit history, revenue, and time in business. If you don’t meet these criteria, accessing financing may be more challenging or result in higher interest rates. 4. Limited funds: The amount of financing you can access is typically limited by your business’s assets, cash flow, or collateral. If your business doesn’t have sufficient assets or cash flow to secure the desired amount of financing, you may need to explore other options or consider alternative financing solutions. In conclusion, financing can be a valuable tool for businesses in need of capital but it’s important to consider both the pros and cons before making a decision. It’s also advisable to compare different financing options, consider your business’s financial situation and goals, and seek expert advice to choose the best option that aligns with your needs.4. Factors To Consider When Choosing
When choosing between factoring and financing for your business, it’s essential to consider various aspects to make an informed decision. Here are the key factors you should take into account:
Cash Flow Needs
Determine your business’s immediate and long-term cash flow needs, including the frequency and volume of invoices. Assess whether you require a lump sum upfront payment or ongoing access to funds, as this will help you decide between factoring and financing.
Customer Involvement
Consider how you want to manage customer interactions related to invoice payments. Assess whether you want your customers to be directly involved in the invoice payment process or if you prefer to handle it independently. This will influence your choice between factoring and financing.
Control And Ownership
Evaluate the level of control and ownership you wish to retain over your outstanding invoices. Decide whether you want to maintain control over collections and client relationships or if you are open to transferring ownership to a financing company or factor.
Additional Services
Consider the additional services offered by lenders or factors, such as invoice processing, credit checks on customers, and other value-added services. Assess whether these supplementary services align with your business needs and can provide added benefits to your operations.

Credit: gatewaycfs.com
Frequently Asked Questions For Factoring Vs Financing
What Is The Difference Between Factoring And Financing?
Factoring and financing both allow businesses to receive payment for invoices upfront. However, with factoring, the lender collects the payment directly from the client, while with financing, the business establishes a relationship with the lender and is responsible for collecting the payment.
What Is The Difference Between Factoring And Supplier Financing?
Factoring and supplier financing are similar in that they both allow businesses to collect invoice payments upfront. However, the main difference is that supplier financing creates a relationship between the business and the lender, whereas factoring creates a relationship between the lender and the client.
In supplier financing, the buyer controls the process, while in factoring, the supplier is in charge.
What Are The Disadvantages Of Debt Factoring?
The disadvantages of debt factoring include involving the customer in redirection of payment, creating a mental burden for business owners, and the possibility of losing control over receivables. Creditors that may lead to loss of control.
What Is The Difference Between Lending And Factoring?
Lending involves borrowing money from a lender, while factoring involves selling invoices to a factor. Factors can take ownership of receivables and provide additional services like invoice processing and credit checks. Lending builds a relationship with the lender, while factoring builds a relationship with the factor.
Conclusion
Both factoring and financing are viable options for business owners to collect invoice payments upfront. However, there are slight differences between the two. Factoring involves redirecting payment from the customer, while financing does not involve the customer. Additionally, factoring creates a relationship between the business and the factoring company, whereas financing creates a relationship between the business and the lender.
Depending on your specific needs and preferences, either option can be beneficial for your business.