Advance Factoring is a type of factoring where the factor advances the full invoice value to the business at the time of the sale, instead of advancing only a percentage of the invoice value. Factoring is a financing option that allows businesses to obtain immediate capital based on the future income from accounts receivable or business invoices.
Advanced Factoring differs from other forms of factoring in that the factor pays the full invoice amount upfront, mitigating the risk of non-payment or late payment for the business. This type of factoring provides businesses with immediate cash flow and eliminates the need to wait for customers to make payment.
However, it can be a more expensive financing option due to the risks assumed by the factoring company.

Credit: www.amazon.com
What Is Advance Factoring?
Advance factoring is a type of invoice financing where a business sells its accounts receivables (unpaid invoices) to a third-party financial company known as a factor. In advance factoring, the factor provides immediate cash advances to the business, typically around 70-90% of the invoice value, while they wait for their customers to pay.
Definition
Advance factoring, also known as full advance factoring, is a financing solution where the factor advances the full value of the invoice to the business at the time of the sale. This allows businesses to access the cash flow they need to cover operating expenses, invest in growth, and manage their day-to-day operations.
Benefits
Advance factoring offers several benefits to businesses:
- Improved cash flow: By receiving immediate cash from the factor, businesses can meet their financial obligations, pay suppliers, and invest in growth without waiting for customers to pay.
- Reduced risk: The factor takes on the responsibility of collecting invoices, reducing the risk of non-payment or late payment. This allows businesses to focus on their core operations and growth strategies.
- Flexible financing: Advance factoring provides businesses with a flexible financing option that grows with their sales volume. As the business generates more invoices, they can factor them to access additional cash flow.
Challenges
While advance factoring offers significant benefits, there are some challenges businesses may face:
- Cost: Factoring fees can be higher compared to traditional loans or lines of credit. However, this cost is justified by the immediate cash flow and reduced risk factor offers.
- Customer relationships: Some businesses may worry that their customers will view factoring as a sign of financial difficulties. However, factoring is a common practice in many industries, and factors work professionally to maintain positive relationships with the business’s customers.
- Eligibility criteria: Factors may have specific criteria for businesses to qualify for advance factoring. These criteria may include minimum monthly sales volume, specific industry focus, or creditworthiness of the business’s customers.
Despite these challenges, advance factoring can be a valuable financing solution that helps businesses improve their cash flow, manage their working capital, and fuel their growth.

Credit: centerpointsecurities.com
Advanced Factoring Techniques
Discover advanced factoring techniques that can help your business streamline cash flow and boost financial stability. With the ability to advance the full value of invoices at the time of sale, advance factoring provides a quick and efficient way to access capital.
Leave behind the complexities of traditional financing and explore the benefits of advance factoring for your business.
In the world of finance, it’s crucial to have a deep understanding of advanced factoring techniques. These techniques can help businesses unlock the cash tied up in their unpaid invoices, providing much-needed liquidity. In this blog post, we will explore three advanced factoring techniques that every business owner should know: factoring a quadratic-like trinomial, factoring the difference of squares, and factoring a polynomial with four terms.Factoring A Quadratic-like Trinomial
Factoring a quadratic-like trinomial is an essential technique that can simplify complex mathematical expressions. This technique involves finding two binomials whose product equals the given trinomial. Let’s take a look at an example to illustrate this technique: Example: Consider the trinomial: x^2 + 7x + 12 To factor this quadratic-like trinomial, we need to find two binomials whose product equals the given trinomial. We can rewrite the trinomial as: (x + 3)(x + 4) The product of these two binomials indeed equals the original trinomial. Using this technique can help businesses simplify complex mathematical expressions and effectively manage their financial equations.Factoring The Difference Of Squares
The technique of factoring the difference of squares is another powerful tool that can simplify polynomial expressions. This technique involves factoring an expression that can be written as the difference between two perfect squares, such as a^2 – b^2. Let’s look at an example to understand this technique better: Example: Consider the expression: x^2 – 9 To factor the difference of squares, we need to identify the two perfect squares. In this case, we have: (x + 3)(x – 3) The product of these two binomials equals the original expression. By employing this factoring technique, businesses can streamline their financial calculations and make informed decisions.Factoring A Polynomial With Four Terms
Factoring a polynomial with four terms is a technique that can be used to simplify complex equations. When dealing with a polynomial with four terms, businesses aim to find the common factors that can be factored out. Let’s consider an example to illustrate this technique: Example: Consider the polynomial: 2x^3 + 4x^2 + 6x + 8 To factor this polynomial, we need to find the common factors among the terms. In this case, we can factor out 2 from each term, resulting in: 2(x^3 + 2x^2 + 3x + 4) Factoring out the common factor can help businesses simplify a polynomial and analyze its components more effectively. By leveraging these advanced factoring techniques, businesses can simplify complex financial equations and gain a better understanding of their cash flow. Whether it’s factoring quadratic-like trinomials, factoring the difference of squares, or factoring polynomials with four terms, these techniques can prove invaluable in optimizing financial decision-making processes.How Does Factoring Work?
In advance factoring, the factor provides the business with the full value of the invoice at the time of sale, whereas in maturity factoring, only a percentage of the invoice value is advanced. Factoring allows businesses to access immediate capital based on their accounts receivable.
The Advance Rate For Factoring
The advance rate for factoring refers to the percentage of the invoice value that is advanced by the factor to the business at the time of the sale. This rate varies depending on factors such as the creditworthiness of the business’s customers, the industry they operate in, and the volume of invoices being factored. Typically, the advance rate ranges from 70% to 90% of the invoice value.Difference Between Maturity Factoring And Advance Factoring
Maturity factoring and advance factoring are two different types of factoring arrangements that businesses can opt for. The main difference between the two lies in the timing of the funds disbursed to the business. In advance factoring, the factor advances the full invoice value to the business at the time of the sale. This means that the business receives immediate access to the funds tied up in their invoices, which can be beneficial for managing cash flow and covering immediate expenses. On the other hand, in maturity factoring, the factor advances only a percentage of the invoice value to the business at the time of the sale, typically ranging from 70% to 90% of the invoice value. The remaining balance is paid to the business when the customer settles the invoice, which is usually within a specified period, such as 30, 60, or 90 days. The choice between maturity factoring and advance factoring depends on the business’s specific cash flow needs and preferences. While advance factoring provides immediate access to funds, maturity factoring can be a more cost-effective option for businesses that can afford to wait for payment on their invoices. In conclusion, understanding how factoring works is essential for businesses looking to optimize their cash flow and manage working capital efficiently. The advance rate for factoring determines the percentage of the invoice value that the factor advances to the business. Additionally, knowing the difference between maturity factoring and advance factoring helps businesses choose the most suitable option based on their specific requirements.Risks And Benefits Of Factoring
When considering options to improve cash flow, businesses often weigh the risks and benefits of factoring. Factoring, commonly known as accounts receivable financing, offers a way for companies to convert outstanding invoices into immediate cash. However, businesses must carefully assess the potential drawbacks and advantages of factoring to make informed decisions about their financial strategies.
Risks Of Factoring
Businesses engaging in factoring should be aware of the potential risks involved. Key risks of factoring include:
- Limited Control: Surrendering customer relationships and collection processes to the factoring company may limit businesses’ control.
- Cost: Factoring can incur higher costs compared to other forms of financing, as factoring companies charge fees, which can impact profit margins.
- Customer Perception: Some clients may perceive the use of a factor as a sign of financial instability, potentially damaging business relationships.
- Risk of Non-Payment: Factoring companies take on the responsibility of collecting invoices, bearing the risk of non-payment or late payment from customers.
Benefits Of Factoring To Improve Cash Flow
Despite the risks, factoring also offers several benefits that can improve a company’s cash flow. Benefits of factoring to improve cash flow include:
- Immediate Cash Infusion: Factoring provides an immediate infusion of cash, enabling businesses to meet their financial obligations promptly.
- Enhanced Working Capital: By converting accounts receivable into cash, factoring improves working capital, enabling businesses to invest in growth opportunities or manage day-to-day operations more effectively.
- Reduced Bad Debt Exposure: Factoring companies assume the responsibility of collecting invoices, reducing the risk of bad debt exposure for businesses.
- Flexible Financing Option: Factoring offers a flexible financing option that isn’t tied to credit ratings or historical financial performance, making it a viable solution for businesses with less established credit profiles.
Examples And Case Studies
Factoring plays a crucial role in providing businesses with immediate access to cash by allowing them to sell their accounts receivables at a discount. Below are some case studies and examples that illustrate the application of advance factoring in different scenarios.
The Algebros
One of the most common applications of advance factoring is in the field of algebraic expressions, often demonstrated in educational videos such as ‘The Algebros’. In this series, viewers are shown various examples of factoring techniques, including factoring polynomials with four terms and identifying perfect squares. These real-world examples help to simplify complex algebraic expressions, making it easier for students to understand and apply these advanced factoring techniques in their studies.
Hill
‘Hill’ is another educational resource that delves into advanced factoring techniques, particularly focusing on the process of factoring with u-substitution and factoring out the greatest common factor. By presenting step-by-step explanations and examples, ‘Hill’ helps learners grasp the principles of advanced factoring and apply them effectively in problem-solving scenarios.
Furthermore, understanding the different advance rates for factoring is essential for businesses seeking immediate cash flow solutions. Advanced factoring allows businesses to access the full invoice value at the time of sale, enabling them to address immediate financial needs with no waiting period. In contrast, maturity factoring only advances a percentage of the invoice value at the time of sale, with the remaining balance paid when the invoice is due. This distinction is critical for businesses in managing their cash flow and financial planning.
Another aspect to consider when evaluating advance factoring is the level of risk involved. Factoring companies assume the responsibility of collecting invoices, which poses a potential risk of non-payment or late payment. This risk, along with the associated costs, needs to be carefully assessed by businesses considering advance factoring as a financing option. Understanding the risks and benefits associated with factoring is essential for making informed financial decisions.
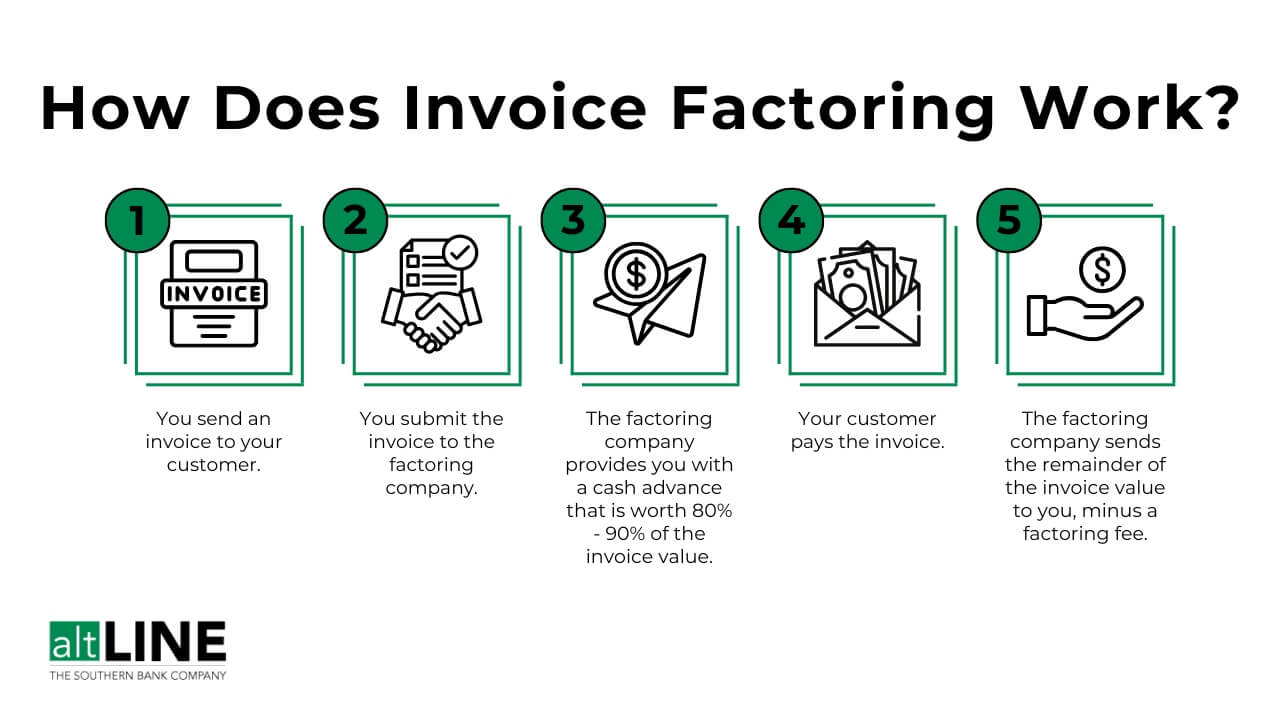
Credit: altline.sobanco.com
Frequently Asked Questions On Advance Factoring
What Is The Advance Rate For Factoring?
The advance rate for factoring is the percentage of the invoice value that the factor advances to the business at the time of the sale. In advance factoring, the factor advances the full invoice value to the business upfront.
What Is The Difference Between Maturity Factoring And Advance Factoring?
In advance factoring, the factor advances the full invoice value to the business at the time of the sale. In maturity factoring, the factor advances only a percentage of the invoice value to the business at the time of the sale, with the remaining balance paid when the invoice becomes due.
How Risky Is Factoring?
Factoring can be more expensive than other forms of financing due to the risk involved. Factoring companies take on significant risks when they purchase invoices, including the responsibility of collecting payments and the risk of non-payment or late payment.
How Does A Factoring Loan Work?
A factoring loan allows a business to get immediate capital based on future income from accounts receivable. It’s a way to access funds owed by customers for credit sales. The factor advances money against invoices, taking responsibility for their collection.
Conclusion
Advance factoring is a beneficial financial tool for businesses seeking immediate capital based on their accounts receivable. Unlike other forms of financing, factoring carries certain risks for the factoring companies, such as non-payment or late payment. However, the advance factoring option allows businesses to receive the full value of their invoices at the time of sale, providing a quick and easy process for improving cash flow.
By understanding the difference between advance factoring and other factoring methods, businesses can make informed decisions to enhance their financial stability.